K9-ACV: A Customized Cancer Vaccine for Dogs
Experimental Autologous Cancer Vaccines created by Ardent Animal Health are provided under 9 CFR 103.3 via USDA Center for Veterinary Biologics oversight for use under supervision/prescription of a licensed veterinarian. Safety & efficacy have not been established.
A Personalized Approach to Canine Cancer
K9-ACV stands for Canine Autologous Cancer Vaccine. Using the therapeutic approach of immunotherapy, our scientists have developed a cancer vaccine, created personally for your pet that can be incorporated in your pet’s cancer treatment plan. Our hope is that K9-ACV will improve and extend the quality of life for your dog.K9-ACV is designed for all operable canine tumors.

Is this an option for your dog?
Why K9-ACV?
Cancer cells can be recognized as foreign by the immune system if those cancer cells are presented to the immune system in a manner that “breaks immune tolerance.” Decades of research in mouse and human models have shown that tumor cells are very much like normal cells in that they express self-antigens that the body is taught to ignore early in development and throughout life. An immunosuppressive environment produced by growing tumors promotes an immune response toward the tumor that is ineffective, allowing the tumor to grow unchecked.
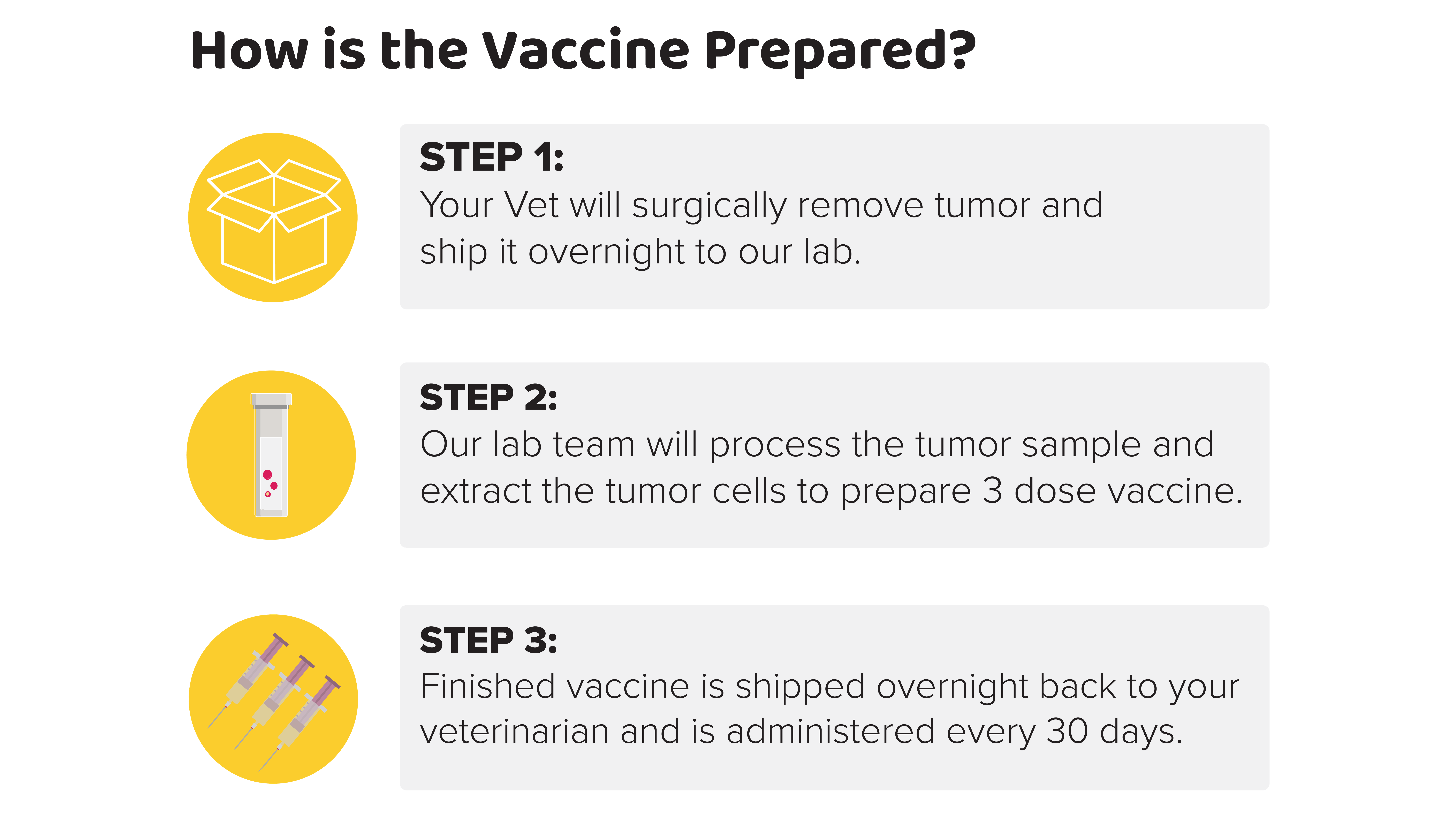

WHAT IS THE ADMINISTRATION PROTOCOL?
WHAT SIDE EFFECTS SHOULD THE OWNER BE MADE AWARE OF?
Safety and efficacy have not yet been established for use in canine patients. In similar human tumor vaccine studies, hundreds of vaccines have been administered on an out-patient basis. Following vaccination, patients are normally observed for roughly 1 hr. for any adverse event which in the experience of the investigators has been minor. Minor fever and minimal inflammation may occur over the next 48 hours. This inflammatory response is beneficial for the success of the vaccine.
ONCE THE TREATMENT PROTOCOL IS UNDERWAY, WHAT WILL MY ROLE BE IN THE DIAGNOSTICS TO ASSIST THE PATIENT?
Once the vaccine is administered, your role will be to monitor the dog’s health, behavior and quality of life.
Cancer in Dogs

While cancer screening programs for early detection in humans have led to significant reductions in cancer deaths, cancer screening for early detection in dogs lags far behind what is available for humans. Consequently, canine cancers are usually diagnosed in later stages of disease, making them more difficult to treat effectively and increasing the likelihood of tumor recurrence. Appropriately designed tumor vaccines can break immune tolerance, leading to an effective anti-tumor immune response which can improve survival and quality of life in veterinary patients. Melanoma in humans has been shown to be quite immunogenic and accordingly immunotherapeutic approaches for cancer have shown promise for melanoma, as well as for other immunogenic tumors. The early work of scientists at the NCI and other centers around the world has led to FDA approval of the first and only therapeutic human cancer vaccine in 2010.
Individual molecule-targeted vaccines require precise knowledge of the targeted molecules before vaccine development can be pursued. Given that many (if not all) tumors can be recognized by the immune system, a broader and possibly better approach for vaccine development may be to use the entire tumor cell (autologous tumor) as the basis for the vaccine and to deliver it to patients in a manner that breaks tolerance to tumor cell antigens and promotes strong anti-tumor immunity.
